Temperature sensor
Consulter nos stocks
PRESENTATION
There are a multitude of temperature sensors, both in their techniques and by their shapes. They are used in many fields both industrial and domestic. Appliances (oven, refrigerator, …), automotive (engine, compartment), the processing industry (plastics, food, chemicals, automotive, electronics, …) and industrial or district heating plants.
In the family of temperature sensorsthere are the thermocouples and RTDs:
- Thermocouples create an electromotive force (mV) when the hot junction (point in contact with the heat source) is different from the cold junction (reference point). This value corresponds to a temperature following an international standard. An electronic circuit converts the value to display temperature (temperature gauge) and / or control (temperature control). There are J thermocouples (iron / constantan), K (nickel chromium / nickel alloy), S (platinum / platinum-rhodium), …
- The RTDs use the variation in resistivity of a material according to the temperature. Measured values ​​(ohms) match temperatures following an international standard. The information is retrieved by an indicator and / or temperature control. There are standard platinum probes (PT 100), thermistor probes …
The majority of existing regulators can interpret the thermocouples (J, K, …) or temperature sensors (PT100) after having preprogrammed.
Temperature range
The temperature range of thermocouples and platinum probe is given by the table below. Depending on the temperature of use and the application domain, choose the appropriate type of construction (see the different models).
|
type |
Positive |
Negative |
Temperature |
|
Thermocouple J |
Iron |
Constantan |
0° C / +760° C |
|
Thermocouple K |
Nickel chrome (or Chromel) |
Nickel allié (or Alumel) |
0° C / +1260° C |
|
Platinium Probe |
-200°C / +850°C |
Color Coding
Thermocouple J
| Polarity | Norm IEC 584* |
Former norme AFNOR |
Former norm DIN |
Former norm ANSI |
|
| Iron | + | Black | Yellow | Red | White |
| Constantan | – | White | Black | Blue | Red |
Thermocouple K
| Polarité | Norme IEC 584* |
Ancienne norme AFNOR |
Ancienne norme DIN |
Ancienne norme ANSI |
|
| Chromel | + | Green | Yellow | Red | Yellow |
| Alumel | – | White | Purple | Green | Red |
* IEC 584 : International Electrical Component
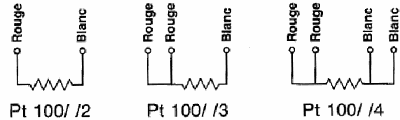
Platinium Probe
Connexion
Tolerances
Thermocouples (Class 2)
| Thermocouples | |
| J | ±2.5°C (±4.5°F) de 0 à 330°C (32 à 626°F) ±0.75 % de 330°C à 760°C (626 à 1400°F) |
| K | ±2.5°C (±4.5°F) de 0 à 330°C (32 à 626°F) ±0.75 % de 330°C à 1260°C (626 à 2300°F) |
Platinium probe 100 Ohms à 0°C (classe B)
| Temperature °C | Tolerance IEC 751:1983 (NF C 42-330, DIN 43790, BS 1904) |
|||
| CLASS A | CLASS B | |||
| ± C° | ± Ohms | ± C° | ± Ohms | |
| -200 | 0.55 | 0.24 | 1.3 | 0.56 |
| -100 | 0.35 | 0.14 | 0.8 | 0.32 |
| 0 | 0.15 | 0.06 | 0.3 | 0.12 |
| 100 | 0.35 | 0.13 | 0.8 | 0.30 |
| 200 | 0.55 | 0.20 | 1.3 | 0.48 |
| 300 | 0.75 | 0.27 | 1.8 | 0.64 |
| 400 | 0.95 | 0.33 | 2.3 | 0.79 |
| 500 | 1.15 | 0.38 | 2.8 | 0.93 |
| 600 | 1.35 | 0.43 | 3.3 | 1.06 |
| 650 | 1.45 | 0.46 | 3.6 | 1.13 |
| 700 | – | – | 3.8 | 1.17 |
| 800 | – | – | 4.3 | 1.28 |
| 850 | – | – | 4.6 | 1.34 |







